[ad_1]
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that impacts millions of individuals globally. Understanding diabetes, its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies is crucial for leading a healthier life. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deeply into diabetes, unravel its complexities, and provide actionable insights for a healthier lifestyle. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, caring for someone with diabetes, or simply seeking to understand the condition better, this article aims to be your ultimate resource.
Understanding Diabetes: Types and Causes
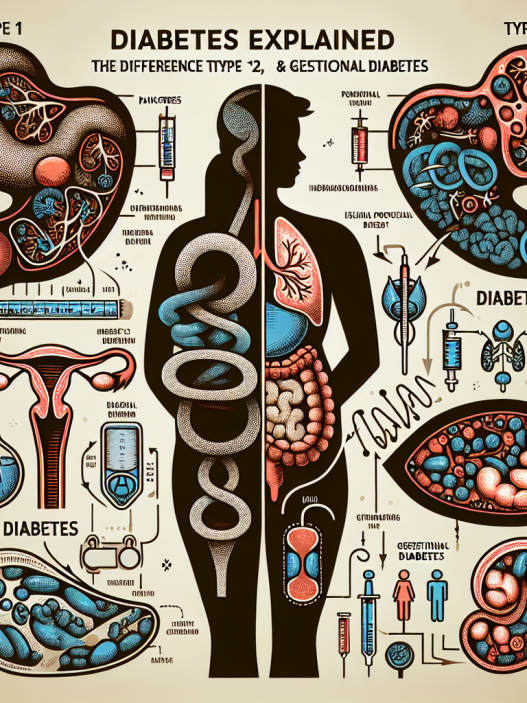
Diabetes is primarily classified into three types: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Although the exact cause is not fully understood, genetic factors and possibly viral triggers are believed to play a role. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes often experience symptoms early in life, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss.
On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is more prevalent and is often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor dietary habits. In this condition, the body either becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce sufficient insulin, posing risks for both the mother and the baby. Recognizing the risk factors associated with diabetes, such as family history, age, and lifestyle choices, is essential in understanding how to prevent it.
Symptoms of Diabetes: Recognizing the Warning Signs
The symptoms of diabetes can vary based on the type. In Type 1 diabetes, symptoms typically develop suddenly and may include extreme thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Individuals may lose weight due to the body’s inability to use glucose effectively for energy. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes symptoms are often subtle and develop gradually, leading many individuals to overlook them for years. These can include increased hunger, slow-healing sores, frequent infections, and dark patches of skin known as acanthosis nigricans.
In women, symptoms may also extend to urinary tract infections and vaginal infections. As diabetes progresses, more severe symptoms may emerge, indicating the need for immediate medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms early on can lead to timely diagnosis and management, significantly reducing the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Complications of Diabetes: The Importance of Early Detection
Diabetes can lead to a multitude of complications, often resulting from prolonged elevated blood sugar levels. Common complications include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke, are more prevalent in individuals with diabetes due to increased risk factors, including hypertension and abnormal cholesterol levels.
Additionally, kidney damage, also known as diabetic nephropathy, occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the filtering system of the kidneys. Over time, this can lead to kidney disease or end-stage renal failure, necessitating dialysis or kidney transplantation. Furthermore, neuropathy, or nerve damage, commonly manifests as tingling, pain, or numbness, often affecting the feet and hands. It’s crucial to manage blood sugar levels effectively and receive regular medical check-ups to mitigate these risks.
The Role of Diet in Managing Diabetes
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. A balanced diabetes-friendly diet consists of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables. Whole grains, such as brown rice and whole wheat bread, help regulate blood sugar levels due to their high fiber content. Fiber is essential as it slows the absorption of sugars in the bloodstream, providing sustained energy and preventing spikes in blood glucose.
Incorporating lean proteins, like fish, chicken, and legumes, helps with satiety and supports overall health. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are vital for heart health—especially important for individuals with diabetes, who are at a higher risk for cardiovascular diseases. It is equally important to monitor carbohydrate intake, opting for complex carbohydrates that have a lower glycemic index to maintain healthier blood sugar levels.
The Benefits of Physical Activity: A Key to Better Blood Sugar Control
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it enhances insulin sensitivity and aids in blood sugar control. Exercise helps the body utilize glucose more effectively, making it a powerful tool in managing diabetes. Even moderate activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can significantly impact one’s health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, combined with strength training exercises two or three times a week.
Beyond physical benefits, exercise also promotes mental well-being. Physical activity releases endorphins, improving mood and reducing stress levels, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals managing the psychological aspects of living with diabetes. Establishing a routine that incorporates both aerobic and resistance training exercises can help maintain optimal blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
Tips for Living a Healthier Life with Diabetes
Living with diabetes requires lifestyle adjustments to promote overall health. Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels is essential to understand how food, activity, and medication affect glucose levels. This awareness can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Additionally, maintaining a consistent meal schedule can help regulate blood sugar levels, making it easier to manage the condition.
Educating oneself about diabetes, including understanding how to read food labels, portion control, and recognizing carbohydrate content, is vital in making healthier choices. Moreover, building a support system can enhance emotional well-being. Connecting with healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, or support groups can provide valuable insights and encouragement throughout the diabetes journey.
Individualized treatment plans are also critical for effectively managing diabetes. Collaborating with healthcare providers to create tailored plans based on personal lifestyle, dietary preferences, and health goals can lead to better outcomes. Incorporating diabetes management into daily life may seem daunting, but creating manageable steps towards a healthier lifestyle is essential.
In conclusion, while diabetes can be daunting, educating yourself about its causes, symptoms, and management techniques can significantly empower you. Prioritizing a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining close communication with healthcare professionals can set the foundation for a healthier life with diabetes. Remember, every small step taken towards understanding and managing your health can lead to a brighter, healthier future.
[ad_2]